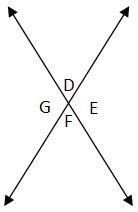
Intersecting Lines
When two lines intersect, they form four angles. Angles that are not adjacent (i.e., do not share a common side) are called vertical angles and these angles are congruent (or equal in measurement).
Due to the properties of intersecting lines, vertical angles are congruent. Consequently, angle D = angle F and angle G = angle E.
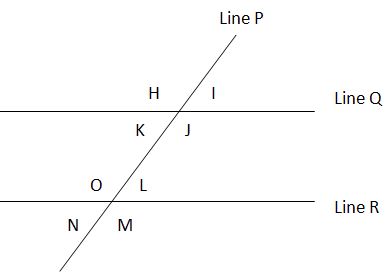
Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal
When two parallel lines are cut by a transversal (i.e., a third line intersects the two parallel lines), a number of relationships exist between the resulting angles.
Alternate Interior Angles Are Equal: K = L; O = J
Alternate Exterior Angles Are Equal: H = M; N = I
Corresponding Angles Are Equal: K = N; J = M; H = O; I = L
Non-Alternate Interior Angles Are Supplementary: L + J = 180; K + O = 180
It is important to note that if two lines cut by a transversal have any of the above properties, then the two lines must be parallel. For example, if alternate interior angles are equal, then the two lines cut by a transversal must be parallel.
Sum of Angles
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is 180 × (n - 2) where n is the number of sides. For example, the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180 = (180)(3 - 2) while the sum of the interior angles of a square is 360 = (180)(4 - 2).