Lesson: Chapter - 14
Energy, Power, and Heat
As a charge carrier moves around a circuit and drops an amount of potential,
V, in time
t, it loses an amount of potential
energy, qV. The power, or the rate
at which it loses energy, is qV/t.
Since the current, I, is equal to
q/t, the power can be expressed as:
P = IV
div>
The unit of power is the watt (W).
As you learned in Chapter 4, one watt is equal to one joule per second.
VIR and PIV Triangles
Ohm’s Law and the formula for power express fundamental relationships between
power, current, and voltage, and between voltage, current, and resistance. On
occasion, you may be asked to calculate any one of the three variables in these
equations, given the other two. As a result, good mnemonics to remember are the
VIR and PIV triangles:
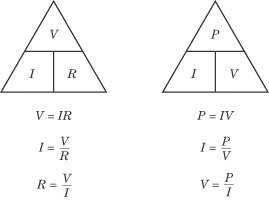
If the two variables you know are across from one another, then multiplying them
will get you the third. If the two variables you know are above and below one
another, then you can get the third variable by dividing the one above by the
one below. For instance, if you know the power and the voltage in a given
circuit, you can calculate the current by dividing the power by the voltage.
Power and Resistance
We can combine the equations for power and Ohm’s Law to get expressions for
power in terms of resistance:

Heat
As current flows through a resistor, the resistor heats up. The heat in joules
is given by:
H = I2 Rt = Pt
where t is the time in seconds. In
other words, a resistor heats up more when there is a high current running
through a strong resistor over a long stretch of time.
Example
A circuit with a potential difference of 10 V is hooked up to a light bulb whose
resistance is 20
O.
The filament in the light bulb heats up, producing light. If the light bulb is
left on for one minute, how much heat is produced?
We are being asked for the amount of heat that is dissipated, which is the
product of power and time. We have learned to express power in terms of voltage
and resistance in the formula P = V2/R. Applying that formula to the
problem at hand, we find:

Then, plugging the appropriate numbers into the equation for heat, we find:
H = Pt = (5W)(60 s) = 300 J
Every minute, the filament produces 300 J
of heat.
Kilowatt-Hours
When electric companies determine how much to charge their clients, they measure
the power output and the amount of time in which this power was generated. Watts
and seconds are relatively small units, so they measure in kilowatt-hours, where
one kilowatt is equal to 1000 watts. Note
that the kilowatt-hour, as a measure of power multiplied by time, is a unit of
energy. A quick calculation shows that:

Next to display next topic in the chapter.
Practice Questions
Video Lessons and 10 Fully Explained Grand Tests
Large number of solved practice MCQ with explanations. Video Lessons and 10 Fully explained Grand/Full Tests.