Lesson: Chapter - 12
Heat Engines
A heat engine is a machine that converts heat into work. Heat engines are
important not only because they come up on Physics, but also because a
large number of the machines we use—most notably our cars—employ heat engines.
A heat engine operates by taking heat from a hot place, converting some of that
heat into work, and dumping the rest in a cooler heat reservoir. For example,
the engine of a car generates heat by combusting gasoline. Some of that heat
drives pistons that make the car do work on the road, and some of that heat is
dumped out the exhaust pipe.
Video Lesson - Heat Engine
Assume that a heat engine starts with a certain internal energy
U, intakes heat
?Qin
from a heat source at temperature
Tin,
does work
?W,
and exhausts heat
?Qin
into a the cooler heat reservoir with temperature
Tout.
With a typical heat engine, we only want to use the heat intake, not the
internal energy of the engine, to do work, so
?U = 0.
The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us:
?U = 0 = ?Qin - ?Qout - ?W
To determine how effectively an engine turns heat into work, we define the
efficiency,
e, as the ratio of
work done to heat input:
div>
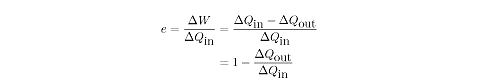
Because the engine is doing work, we know that
?W
> 0, so we can conclude that
?Qin
>
?Qout.
Both
?Qin
and
?Qout
are positive, so the efficiency is always between 0 and 1:
0 = < 1
Efficiency is usually expressed as a percentage rather than in decimal form.
That the efficiency of a heat engine can never be 100% is a consequence of
the Second Law of Thermodynamics. If there were
a 100% efficient machine, it would be
possible to create perpetual motion: a machine could do work upon itself without
ever slowing down.
Example
80 J of heat are injected into a heat engine, causing it to do work. The engine
then exhausts 20 J of heat into a cool reservoir. What is the efficiency of the
engine?
If we know our formulas, this problem is easy. The heat into the system is
?Qin
= 80 J, and the heat out of the system is
?Qout
= 20 J. The efficiency, then, is:
1 – 20 / 80 = 0.75 = 75%.
Next to display next topic in the chapter.
Practice Questions
Video Lessons and 10 Fully Explained Grand Tests
Large number of solved practice MCQ with explanations. Video Lessons and 10 Fully explained Grand/Full Tests.