Lesson: Chapter - 10
Kinetic Energy
There is a certain amount of energy associated with the rotational motion of a body, so that a ball rolling down a hill does not accelerate in quite the same way as a block sliding down a frictionless slope. Fortunately, the formula for
rotational kinetic energy, much like the formula for translational kinetic energy, can be a valuable problem-solving tool.
The kinetic energy of a rotating rigid body is:
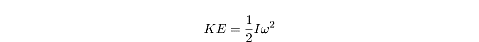
Considering that I is the rotational equivalent for mass and ? is the rotational equivalent for velocity, this equation should come as no surprise.
An object, such as a pool ball, that is spinning as it travels through space, will have both rotational and translational kinetic energy:

In this formula, M is the total mass of the rigid body and vcm is the velocity of its center of mass.
This equation comes up most frequently in problems involving a rigid body that
is rolling along a surface without sliding. Unlike a body sliding along a
surface, there is no kinetic friction to slow the body’s motion. Rather, there
is static friction as each point of the rolling body makes contact with the
surface, but this static friction does no work on the rolling object and
dissipates no energy.
Example
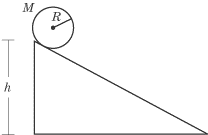
A wheel of mass M and radius R is released from rest and rolls to
the bottom of an inclined plane of height h without slipping. What is its
velocity at the bottom of the incline? The moment of inertia of a wheel of mass
M and radius R rotating about an axis through its center of mass
is 1/2 MR2
Because the wheel loses no energy to friction, we can apply the law of
conservation of mechanical energy. The change in the wheel’s potential energy is
–mgh. The change in the wheel’s
kinetic energy is
 .
Applying conservation of mechanical energy:
.
Applying conservation of mechanical energy:

It’s worth remembering that an object rolling down an incline will pick up speed
more slowly than an object sliding down a frictionless incline. Rolling objects
pick up speed more slowly because only some of the kinetic energy they gain is
converted into translational motion, while the rest is converted into rotational
motion.
Next to display next topic in the chapter.
Practice Questions
Video Lessons and 10 Fully Explained Grand Tests
Large number of solved practice MCQ with explanations. Video Lessons and 10 Fully explained Grand/Full Tests.