Lesson: Chapter - 5
Charles’s Law
Charles’s law states that if a given quantity of gas is held at a constant
pressure, its volume is directly proportional to the absolute temperature. Think
of it this way. As the temperature of the gas increases, the gas molecules will
begin to move around more quickly and hit the walls of their container with more
force—thus the volume will increase.
Keep in mind that you must use only the
Kelvin temperature scale when working with temperature in all gas law
formulas! Here’s the expression of Charles’s law that you should memorize:
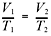
Try using Charles’s law to solve the following problem.
Example
A sample of gas at 15ºC and 1 atm has a volume of 2.50 L. What volume will this
gas occupy at 30ºC and 1 atm?
Explanation
The pressure remains the same, while the volume and temperature change—this is
the hallmark of a Charles’s law question.
So,
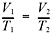
then 2.50 L/288K = V2/303K, and V2 = 2.63 L
This makes sense—the temperature is increasing slightly, so the volume should
increase slightly. Be careful of questions like this—it’s tempting to just use
the Celsius temperature, but you must first convert to Kelvin temperature (by
adding 273) to get the correct relationships!
Next to display next topic in the chapter.
Practice Questions
Test Prep Lessons With Video Lessons and Explained MCQ
Large number of solved practice MCQ with explanations. Video Lessons and 10 Fully explained Grand/Full Tests.