The Electric Generator
The electric generator, sometimes called a “dynamo,” is a noisy favorite
at outdoor events that need electricity. It uses the principle of
electromagnetic induction to convert mechanical energy—usually in the form of a
gas-powered motor—into electrical energy. A coil in the generator rotates in a
magnetic field. As the magnetic flux through the coil changes, it induces an
emf, creating a current.
The Transformer
The transformer converts current of one voltage to current of another
voltage. A simple transformer consists of two coils wrapped around an iron core.
Transformers rely on the property of mutual induction: the change in
current in one coil induces an emf in another coil. The coil with the applied
current is called the primary coil, and the coil with the induced emf is called
the secondary coil.

The induced emf is related to the emf in the primary coil by the number of turns
in each coil:
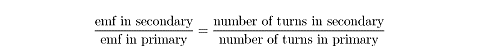
Outside a power plant, a “step-up” transformer, whose primary coil has fewer
turns than its secondary coil, increases the voltage (emf) of the current that
is transported along power lines. Then, before the power enters your house, a
“step-down” transformer, whose secondary coil has fewer turns than its primary
coil, reduces the voltage. The higher voltage on power lines cutting across the
countryside allows more electricity to be transported quickly to urban centers.
The lower voltage within your house renders the electricity safer.
Back
Next
div>
Next to display next topic in the chapter.
Practice Questions
Video Lessons and 10 Fully Explained Grand Tests
Large number of solved practice MCQ with explanations. Video Lessons and 10 Fully explained Grand/Full Tests.